The sun, a massive ball of gas and plasma, has been the center of our solar system for billions of years.
It is a source of light, heat, and energy that sustains life on Earth. However, despite its importance, there is still much to be discovered about this powerful star.
That is why NASA, the leading space exploration agency, has set its sights on a monumental mission - landing on the Sun.
NASA spacecraft set to attempt landing on the Sun
As dubbed a "monumental achievement for humanity equivalent to the moon landing," NASA has announced its plans to send a spacecraft to land on the sun's surface.
This ambitious mission, known as the Parker Solar Probe, is set to launch within the year and journey 3.8 million miles into space, brushing past the sun's molten surface at an astonishing speed of 435,000 mph.
This will be the closest a man-made object has ever reached to the surface of the sun, making it a groundbreaking feat in the history of space exploration.
The probe will not only be the first of its kind to land seven times closer to the sun than any other craft in humanity's history, but it will also obtain the first-ever sampling of a star's atmosphere.

The scientist Nour Raouafi told BBC: "This will be a monumental achievement for all humanity. This is equivalent to the Moon landing of 1969."
"We are basically almost landing on a star," he explained.
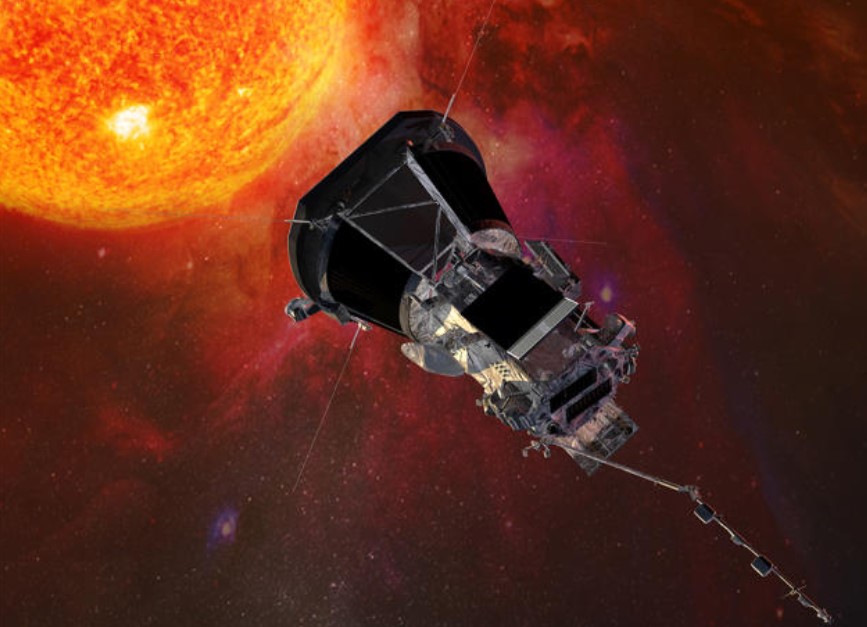
Spacecraft sent to the Sun: The Parker Solar Probe
NASA has been planning this mission for over six decades.
The first concept of a spacecraft reaching the sun was proposed by physicist Eugene Parker in the 1950s, and it has taken several decades of technological advancements and scientific research to make it a reality.
The Parker Solar Probe, named after the pioneering scientist, is a specially designed spacecraft that can withstand extreme heat and radiation from the sun.

It is equipped with a state-of-the-art heat shield made of carbon-carbon composite material, which can withstand temperatures up to 2,500 degrees Fahrenheit.
This shield will protect the spacecraft's instruments and electronics from melting as it gets closer to the sun.
Sun landing mission by NASA
The Parker Solar Probe's mission is not just about landing on the sun's surface; it is also about gathering crucial data and information that will help scientists better understand the sun and its effects on our solar system.
The probe will gather photographs and measurements of the sun's atmosphere, magnetic fields, and solar winds, providing valuable insights into the star's behavior.
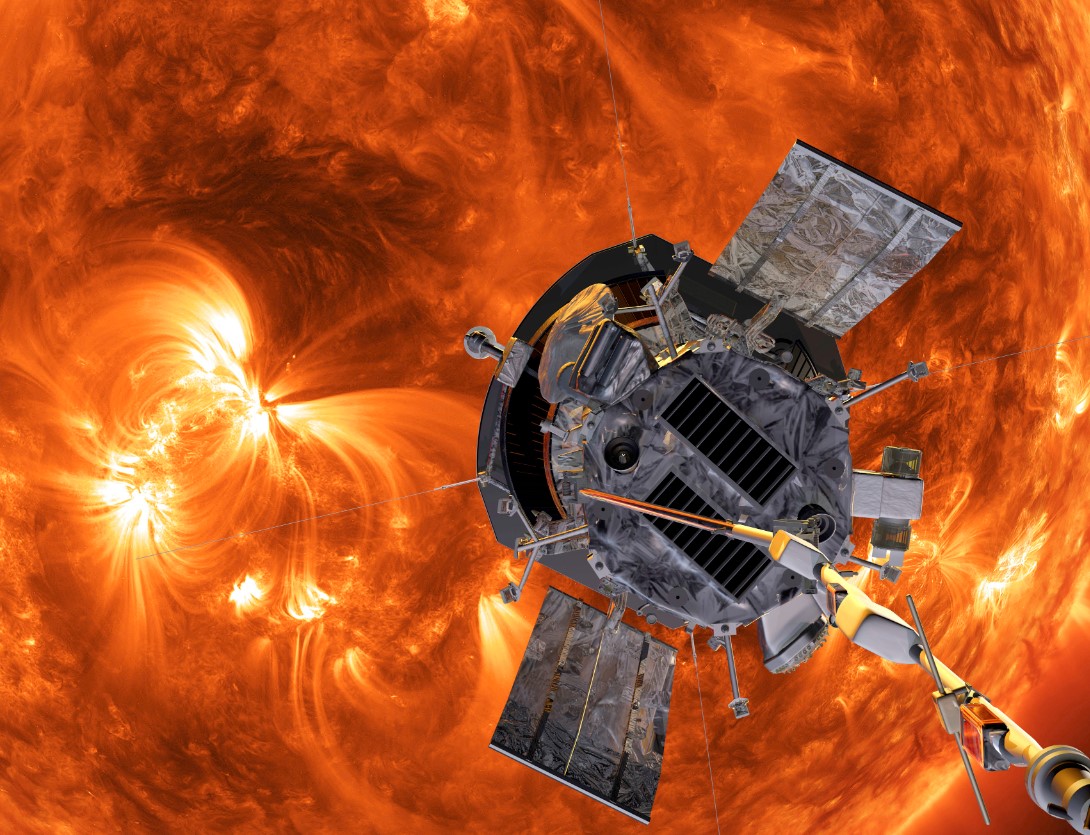

One of the key objectives of the mission is to study the sun's corona, the outermost layer of its atmosphere.
This region is where solar winds are generated, and understanding its dynamics is crucial for predicting space weather events that can affect Earth's communication systems and power grids.
The data collected by the Parker Solar Probe will also help scientists develop better models and theories about the sun's structure and evolution.






