Many people are only now beginning to understand the differences between FM and AM radio.
In the age of digital broadcasting and smartphones, traditional radio may seem outdated.However, many still find themselves puzzled by the differences between FM and AM radio.
Beyond the static interference that often accompanies AM, there are fundamental differences in how these radio signals work.

On Reddit’s platform, many users are discussing the differences between AM and FM radio.
One person said: FM is frequency modulation of signal and AM is amplitude modulation.
A second wrote: FM stands for frequency modulated. AM stands for amplitude modulated.
While a third commented: On FM the radio waves vary in how frequent they are generated and are read based upon that.
On AM the radio waves come with the same exact timing, but they vary in size.
FM standing for Frequency modulation, and AM standing for Amplitude Modulation.

Another added: Ah, Amplitude Modulated vs Frequency Modulated. This makes sense now.
Someone else said: So cool. I had this on my Telecommunication Systems class, and it was so great to be able to understand it. And then the names clicked perfectly in place.
How radio works
To grasp the differences between AM and FM, it’s crucial to understand how radio broadcasts operate.
Radio stations use a carrier signal, which is a constant electromagnetic wave.
This wave has a fixed frequency and amplitude.

When a station broadcasts music or spoken content, it encodes this information into the carrier wave.
Then, this is done by modulating the wave’s frequency and amplitude.
The modified signal is transmitted through large antennas and picked up by radios.
Additionally, the receiver uses a demodulator to decode the signal.
It converts the decoded signal back into sound waves that we can hear.
The difference between AM and FM radio
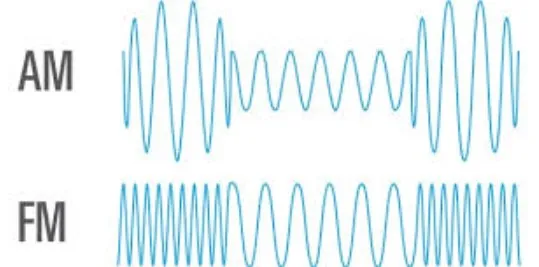
AM (Amplitude Modulation):

AM radio modulates the amplitude of the carrier wave. This means that the height of the wave varies to encode information.
However, AM signals are susceptible to interference from various sources, such as power lines and lightning.
This interference can distort the signal and cause static. It can be startling if you accidentally switch from FM to AM.
FM (Frequency Modulation)
FM radio, on the other hand, adjusts the frequency of the carrier wave to encode information.
Since FM signals are less affected by amplitude interference, they generally provide a clearer sound quality.
The broader bandwidth available for FM signals also contributes to its superior audio clarity.
Why AM Radio is still used
Despite its drawbacks, AM radio remains in use due to its significant advantages.
AM radio waves have longer wavelengths, allowing them to cover a larger broadcast range.
They can penetrate through buildings and reach remote areas more effectively than FM signals.

This broad coverage makes AM valuable for emergency broadcasts and reaching listeners in less accessible regions.
FM radio offers superior sound quality due to its method of modulation. While, AM radio’s extensive range makes it indispensable for certain applications.
Understanding these differences can help listeners appreciate the unique qualities and practical uses of each type of radio broadcast.